Any company is vulnerable to some form of disruption. This may be from hardware failure, theft, human error, natural disasters, or other factors outside your control. The risk of not having a backup strategy doesn’t simply signal data loss. It’s the implications of that data loss that are critical: What would it cost if you lost some or all of your business data?
For many medium-sized to large corporates, losing critical data for even a few days could result in serious losses, reputational and/or financial. Therefore, it is important to prioritize getting a resilient backup strategy for your organization.
1. Threats to Your Business Data
Many concepts factor into a good backup strategy. The challenge is not to build a universal solution but to develop a well-balanced data protection plan that suits your particular needs. Therefore, while including the 3-2-1 backup rule, the plan should cover many other aspects of data protection such as critical data areas, backup types, storage media, scheduling, disaster recovery operation, automation, encryption, regular live testing under different scenarios, etc.
Risks to Business Data Are Everywhere
Reports of malicious software and hackers are everywhere these days. While these threats pose significant risks for businesses, they are also certainly not the only ones out there. With that in mind, we will cover some of the threats that put your business data and at risk daily.
Common threats to business data include:-
- Hackers and ransomware: Cyberattacks against businesses are on the rise and doing more damage than ever. In the last decade, numbers relating to ransomware are on the rise and quite alarming. Beyond the risk of losing money, businesses have a lot more to lose than just data in a cyberattack.
- Viruses, worms, malware: While hackers and ransomware outbreaks are certainly causing damage and making headlines, old-school malware, spyware, and old-fashioned viruses continue to be among the leading causes of system breaches/data loss. Even with updated security software, most businesses remain exposed to the threat of data loss due to hackers, malware, and ransomware.
- Physical disasters: A fire, flood, or building collapse can wipe out all the data in your primary business premises.
- Theft: Theft of company computers or servers, hard drives, or storage device may result in significant data loss.
- Hardware failure/crashes: There is a very real possibility of hard drive failure and other types of hardware mishaps. Electrical faults/voltage surges may also contribute to hardware failure.
- Human error: Business data may be lost owing to simple accidental deletion – sometimes it could be from a single click.
- Vandalism: deliberate destruction and loss resulting from political unrest, demonstrations.
- Acts of Terrorism
With this laundry list of threats, it is not a matter of if your business will become a victim; it’s just a question of when.
2. Backup Strategies
As illustrated above, there are numerous threats to business data. Keeping backup copies of your important files and data is essential to minimize disruption to business in the event of a disaster.
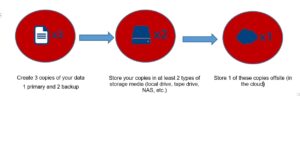
Virtually all computer and technology experts will tell you that any backup strategy is better than none at all. However, not all backup devices and technologies are the same, nor do they all offer the same protection levels. For optimal protection, it is best to safeguard your data using the time-honored 3-2-1 rule. Put simply, the 3-2-1 rule states that you should:
- Keep at least three (3) copies of your data in different locations (so no single event will destroy all copies);
- Store the data in at least two (2) different formats. For instance, external drive, tape, etc.);
- Keep one (1) copy offsite in the cloud to protect against fire, flood, theft, and other physical disasters.
To guide you on how you can implement the 3-2-1 rule, let’s look at some common ways businesses do backups.
2.1 Local Drives and Network Backups
A common way to create backups of business data is by storing copies of files on external media. For instance, hard drives, USB flash drives, tape drives, or other storage devices connected to your systems or network. As with any good data recovery plan, keeping local copies of backups is essential. Backing up to devices attached to computer systems or copying files to devices connected via a local or wide area network is an effective way of ensuring backups are available locally when you need them.
However, due to risks associated with physical disasters, ransomware, theft, and other threats, keeping local backups should never be the only facet of your backup strategy. You should always store at least one copy offsite as is required with the 3-2-1 rule. This may be on an offsite backup server or in the cloud.
2.2 Cloud Backups
These days, wherever you turn, there is talk or news about businesses migrating to the cloud. Essentially, they are running software and systems remotely via the internet. A backup strategy is no exception. Cloud backups are secure, offsite copies of stored data on remote servers and accessed via an internet connection. Cloud backups are an excellent choice for providing additional redundancy and security for businesses that want to ensure their critical data is available when disasters strike.
2.3 Online File Storage
Please note that cloud backups and online file storage are not the same. Several businesses use Dropbox, Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, and other online storage websites to store backup copies of their important files. While these services are okay for storing and sharing a few files, the limitations of online storage sites prevent them from being true cloud backups. A true cloud backup service enables you to create automated backups of complete systems and store as many versions of backups as you need).
3. Data Recovery
Now that you have a backup solution in place, is it good enough to quickly return your business to normal after a disaster? If that solution is only disk or tape, think again. Outdated solutions are simply that: Outdated. It’s important to have a solution that will keep your business prepared for quick recovery or low RTO (Recovery Time Objective) in the face of disruption.
A proper backup solution is only as good as its recovery.
The resiliency of your backup also depends on its security features. Choose a solution that encrypts data in transit and in storage and one that hosts it in a truly secure data center.
4. Conclusion
People tend to think in terms of the probability of disasters affecting their primary business premises. Of course, earthquakes, floods, or tornadoes may be the most unlikely events for your city. You may also think the probability of a terroristic attack is remote, but most of the common threats leading to data loss are always present. Even if your primary business premise is well protected against physical threats, there are still other threats, which are largely not in your control: hardware failure, viruses, malicious attacks, and human error.
There are many ways for businesses to create backups of important data, and you should use multiple methods to ensure your data is always available when needed.
MailSafi offers an easy-to-manage, cost-effective cloud backup solution that enables you to back up entire systems/virtual machines or limit backups to mission-critical data or files. Get in touch to learn more about our solution.
![]()




Pingback: The Golden 3-2-1 Backup Rule – An Efficient Data Protection Strategy » The MailSafi Blog
Pingback: Cybersecurity Awareness Training Topics for 2021 | MailSafi
Pingback: Ransomware: The growing online endemic. What is it? | MailSafi
Pingback: Cloud Email Hosting for Business: The Benefits | MailSafi